CONTACTAbout UsCAREER OPPORTUNITIESADVERTISE WITH USPRIVACY POLICYPRIVACY PREFERENCESTERMS OF USELEGAL NOTICE
© 2025 Equal Entertainment LLC.
All Rights reserved
All Rights reserved
By continuing to use our site, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use.
We need your help
Your support makes The Advocate's original LGBTQ+ reporting possible. Become a member today to help us continue this work.
Your support makes The Advocate's original LGBTQ+ reporting possible. Become a member today to help us continue this work.
A new study by Canadian researchers adds weight to the theory that the evolutionary role of gay men may be to serve as "super uncles" who help close family members survive.
Paul Vasey, an evolutionary psychologist at the University of Lethbridge, sought to address an entrenched scientific riddle: If homosexuality appears to be inherited, how have gay men, who are less likely to reproduce, continued to pass on their genes without becoming extinct?
According to The Gazette of Montreal, one long-running theory argues that gay men serve the evolutionary role of acting as "super uncles" who assist close relatives and indirectly increase the chances of passing on their genes.
"The idea is that homosexuals are helping their close relatives reproduce more successfully and at a higher rate by being helpful: babysitting more, tutoring their nieces and nephews in art and music, and helping out financially with things like medical care and education," reports The Gazette.
Vasey and his colleague Doug VanderLaan tested the theory on the Pacific island of Samoa, where they studied women, straight men, and the fa'afafine, men who prefer other men as sexual partners and are accepted within the culture as a distinct third gender category.
"Vasey found that the fa'afafine said they were significantly more willing to help kin, yet much less interested in helping children who aren't family -- providing the first evidence to support the 'kin selection hypothesis,'" reports The Gazette.
"Maybe it's in this way that they're indirectly passing on at least some of the genes that they're sharing with their kin," said Vasey.
The findings are published online this week in the journal Psychological Science.
Researchers are now exploring whether the fa'afafine actually follow through on their stated willingness to help family members by giving more money to relatives.
From our Sponsors
Most Popular
Bizarre Epstein files reference to Trump, Putin, and oral sex with ‘Bubba’ draws scrutiny in Congress
November 14 2025 4:08 PM
True
Jeffrey Epstein’s brother says the ‘Bubba’ mentioned in Trump oral sex email is not Bill Clinton
November 16 2025 9:15 AM
True
Watch Now: Pride Today
Latest Stories
Is Texas using driver's license data to track transgender residents?
December 15 2025 6:46 PM
Rachel Maddow on standing up to government lies and her Walter Cronkite Award
December 15 2025 3:53 PM
Beloved gay 'General Hospital' star Anthony Geary dies at age 78
December 15 2025 2:07 PM
Rob Reiner deserves a place in queer TV history for Mike 'Meathead' Stivic in 'All in the Family'
December 15 2025 1:30 PM
Culver City elects first out gay mayor — and Elphaba helped celebrate
December 15 2025 1:08 PM
Texas city cancels 2026 Pride after local council rescinds LGBTQ+ protections
December 15 2025 12:55 PM
North Carolina county dissolves library board for refusing to toss book about a trans kid
December 15 2025 11:45 AM
Florida and Texas launch 'legal attack' in push to restrict abortion medication nationally
December 15 2025 11:18 AM
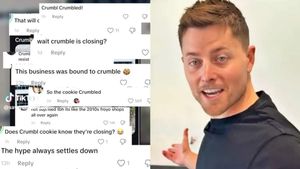
No, Crumbl is not Crumbl-ing, gay CEO Sawyer Hemsley says
December 15 2025 10:12 AM
11 times Donald Trump has randomly brought up his ‘transgender for everybody’ obsession
December 15 2025 9:22 AM
The story queer survivors aren't allowed to tell
December 15 2025 6:00 AM


































































Charlie Kirk DID say stoning gay people was the 'perfect law' — and these other heinous quotes